PHYSIOTHERAPY TECHNIQUES

Joint mobilisation
a passive oscillatory movement technique applied manually by the physiotherapist to a spinal or peripheral joint to decrease pain and increase joint range of movement
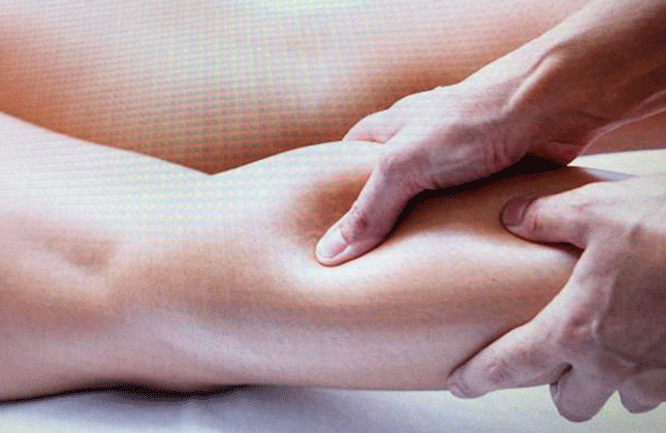
Soft tissue mobilisation
passive techniques applied to the soft tissues like muscles, tendons, ligaments, fascia, nerves and fibrous tissues to decrease pain & tightness and to promote relaxation
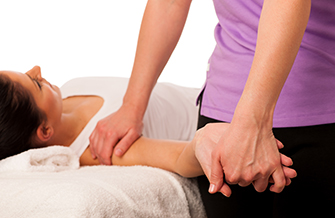
Neural mobilisation
movements to glide the nerve inside its sheath to improve axoplasmic flow in the nerve, in order to decrease pain and to increase mobility
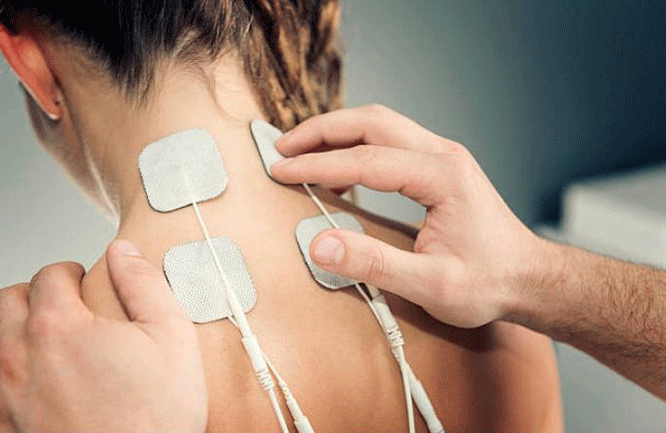
Electrotherapy (ET)
including a variety of modalities like Ultrasound, Interferential, Laser therapy, Deep Oscillation therapy, TENS, Muscle stimulation.
ET is used to aid the healing process, to relieve pain, to reduce swelling and bleeding by increasing the blood circulation to the area and by facilitating the lymph drainage away from the injured area

Respiratory Treatment
consists of percussion, vibration and shaking in specific postural drainage (PD) positions to mobilise lung secretions so that it can be coughed up. Breathing exercises and PEEP are used to improve lung expansion and breathing patterns in a variety of lung conditions and post-operatively. Suctioning consists of using a suctioning machine to mobilise lung secretions when necessary

Neuro-Development Therapy
the use of various inhibitory and stimulative techniques in conjunction with rehabilitation and strengthening in order to overcome the effects of a stroke, spinal cord or other nerve-related injuries and conditions, as well as developmental delays and cerebral palsy in adults and children alike.

Dry needling
the use of needles to relieve pain, muscle spasm and stiffness. Needles are inserted into the affected muscles, causing the release of endorphins to block pain stimuli, to relax the muscle and to increase the blood circulation

Advice
on pain management (pacing and pausing exercises), ergonomics and kinetic handling skills to prevent injuries, reduce pain, aid healing and to improve general health

Strapping & Taping
tape is used to facilitate a muscle or movement or to immobilise a joint to limit pain and further injury or provide joint stability

Rehabilitation Exercises
Variety of exercises is used for
Re-education of muscles (stabilisers)
Strengthening of muscles (movers)
Stretching of muscles & fascia
Mobilising of joints to increase range
Promoting tissue health & to aid healing
Pain management, stress release & relaxation
Improving lung functioning & increasing lung expansion in lung conditions & post-operatively.

Pilates
is a balanced and safe form of exercise for overall body conditioning for anyone with or without injury. Pilates is essentially a mind-body centering technique emphasising the importance of beginning all movements from a central core of stability.
If practiced regularly, Pilates
Trains the core muscles
Corrects postural alignment
Improves flexibility
Builds muscle strength
Correct muscle imbalances
Develops control & endurance
Improves co-ordination, balance, bone density
Increase body-mind awareness
Prevents injuries
Reduces stress & enhances relaxation
Elevates spirit & vitality

Sports and/or Deep tissue massage
passive massage can enhance performance and recovery for the athlete and the non-sports persons. It improves flexibility, keeping the muscles in an optimal physiological condition and thereby reducing the risk of injury and the effects of micro-trauma. Both sports massage and deep tissue massage can alleviate pain which can be caused by too much physical activity, too many bad triggers or stress.
Massage can help DOMS (delayed onset of muscle soreness) that typically occurs 24-48 hours after exercise by increasing the blood and lymph flow through the body.
During a massage the body releases endorphins which relieves pain and helps to decrease stress and anxiety for people functioning in a corporate environment.
